12
August
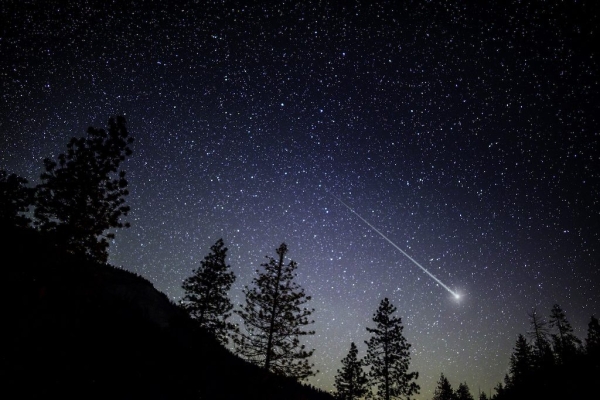
Perseid Meteor Shower Watch 2023 (SOLD OUT)
Come watch the Perseids, one of the best meteor showers of the year, on the open field beside the Rouge Valley Conservation Centre.

22
July
RASCTO Sun Fun at Richmond Hill Public Library
Summer is time for fun in the sun, but what do you really know about our nearest star?

25
July
Stargazing Night - July 2023 (GO for Tuesday)
Bring Your Own Binoculars and observe the sky from the David Dunlap Observatory!

7
October
Solar Observing at Ontario Science Centre - October 2023 (GO for October 6)
Enjoy safe views of the Sun every first Saturday of the month at the Ontario Science Centre!

2
September
Solar Observing at Ontario Science Centre - September 2023 (GO for September 2)
Enjoy safe views of the Sun every first Saturday of the month at the Ontario Science Centre!

5
August
Solar Observing at Ontario Science Centre - August 2023 (GO for August 5)
Enjoy safe views of the Sun every first Saturday of the month at the Ontario Science Centre!

28
June
Stargazing Night - June 2023 (GO for Wednesday)
Bring Your Own Binoculars and observe the sky from the David Dunlap Observatory!

8
July
Solar Observing at Ontario Science Centre - July 2023 (GO for July 8)
Enjoy safe views of the Sun every first Saturday of the month at the Ontario Science Centre!

7
June
The Sky This Month - June 2023
Our resident expert, Chris Vaughan, on all things in Astronomy takes his hand at the Sky This Month for the period of June 7-July 5 2023.

7
May
DDO: Sunday Sungazing - May 2023
Safely observe the sun with us! Join us at the DDO for these family-friendly sessions where a DDO Astronomer will answer your questions about our closest star: the sun!