18
December
New Moon - 1:30am EST
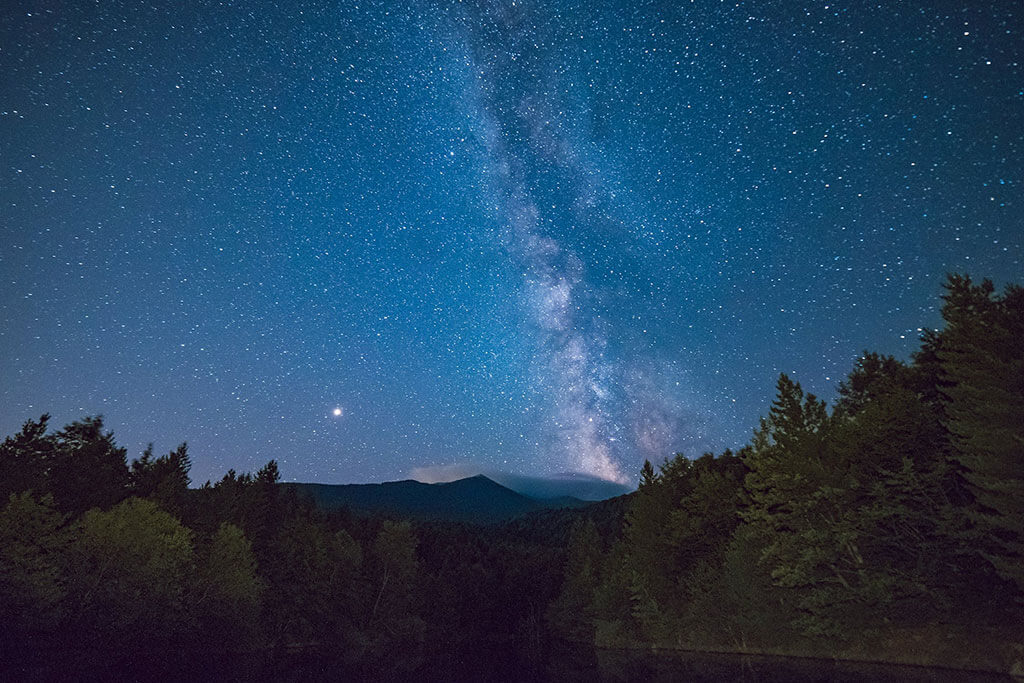
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

18
November
New Moon - 6:42am EST
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

19
October
New Moon - 3:12pm EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

20
September
New Moon - 1:30am EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

21
August
New Moon - 2:30pm EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

23
July
New Moon - 5:46am EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

23
June
New Moon - 10:31pm EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

25
May
New Moon - 3:44pm EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

26
April
New Moon - 8:16am EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.

27
March
New Moon - 10:57pm EDT
The moon is between us and the sun. Without the moon in the sky at night, deep sky objects are easier to observe.